Respiratory physiotherapy: Techniques and benefits for patients withlung disease
Respiratory physiotherapy: Techniques and benefits for patients withlung disease
Respiratory physiotherapy: Techniques and benefits for patients with lung disease
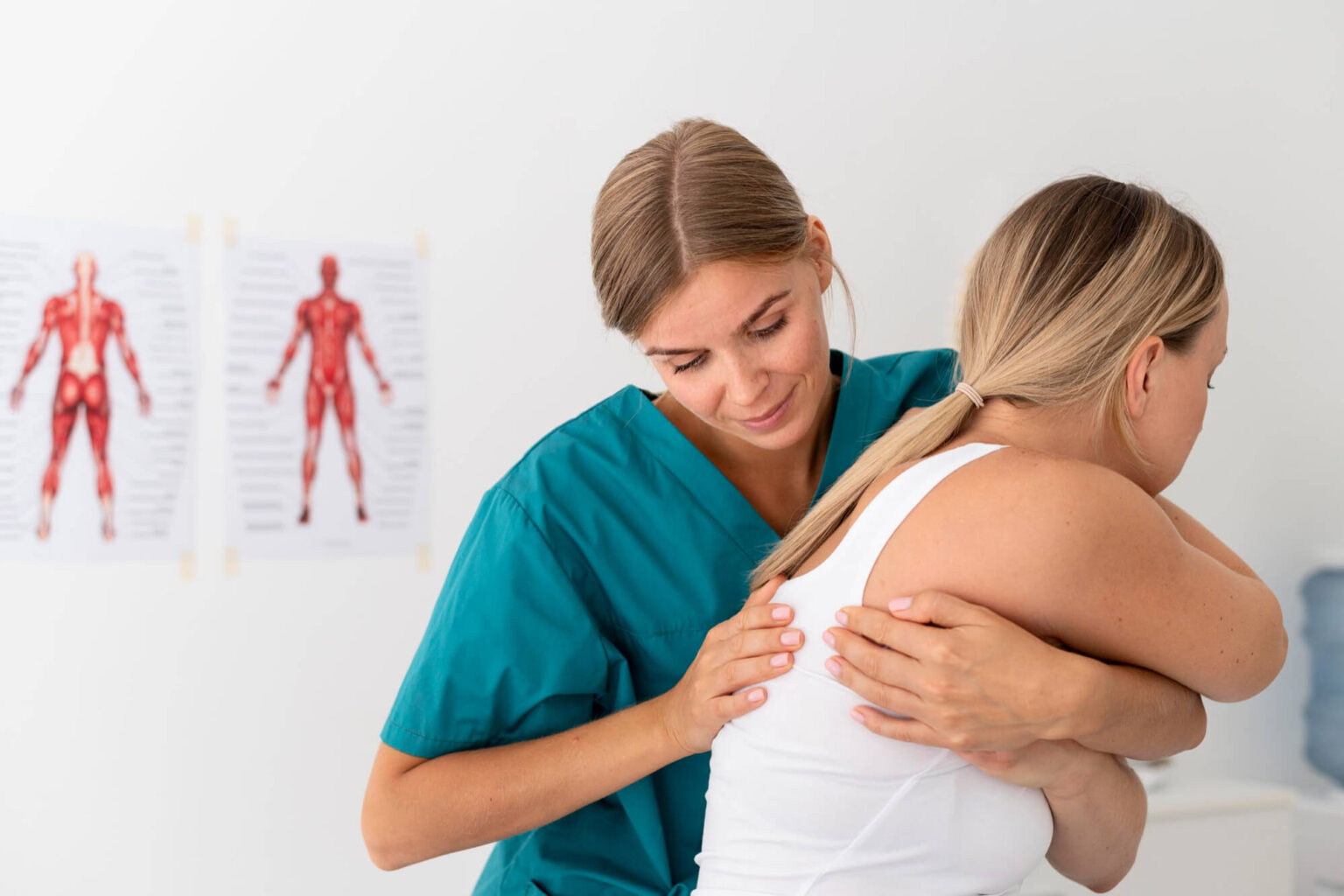
Within general physiotherapy, respiratory physiotherapy is a specialised branch that focuses on the treatment and prevention of respiratory disorders, helping patients with respiratory conditions improve their quality of life.
Recognising both its importance and the need for greater awareness, at Telic we want to talk about what respiratory physiotherapy is, what techniques are used, and the benefits it offers, especially for those with lung conditions.
What is respiratory physiotherapy?
Respiratory physiotherapy is designed to optimise the functioning of the respiratory system, working comprehensively to treat lung disorders and pathologies.
Its aim is to improve pulmonary ventilation, reduce mucus build-up, and increase the respiratory capacity of patients, which results in greater well-being and a higher quality of life.
Because of its complexity, this discipline must be carried out by specialised physiotherapists who have extensive knowledge of the respiratory system.
Treatments vary according to the specific needs of each patient, adapting to the nature of their illness.
It is important to note that respiratory physiotherapy can be provided to both hospitalised patients and those undergoing diagnosis or receiving treatment at home.
The main respiratory physiotherapy techniques
To effectively treat respiratory pathologies, respiratory physiotherapists employ various techniques, each with its own specific objective.
Respiratory exercises
Respiratory exercises are fundamental to improving pulmonary ventilation. These exercises include different breathing and chest expansion techniques, such as diaphragmatic breathing and rib expansion exercises.
- Relaxation techniques: help the patient relax during treatment.
- Diaphragmatic breathing: consists of a slow, deep inhalation through the nose, with the abdomen gradually rising, followed by an exhalation through slightly parted lips, observing how the abdomen slowly descends.
- Chest expansion: during inhalation, the hand is placed on the area to be treated to facilitate expansion of the chest, promoting greater respiratory capacity.
- Belt exercises: a variant of chest expansion exercises, where the patient can perform the technique independently.
Bronchial drainage
Bronchial drainage is designed to eliminate built-up mucus in the bronchial tree. This process improves pulmonary ventilation and aids the expulsion of mucus that may hinder breathing.
- Postural drainage: involves placing the patient in different positions according to the area of the lung that needs to be drained. Each position is held for 3 to 5 minutes, promoting the elimination of mucus.
- Percussion: rhythmic clapping is applied to the patient's chest to help loosen bronchial mucus.
- Vibration: the speed of exhaled air is increased through a discontinuous compression of the chest wall, aiding the expulsion of mucus.
- Huffing and coughing: after performing diaphragmatic breathing, the patient performs a deep and rapid exhalation or a controlled cough to expel built-up mucus.
General physical training
Physical training is an essential part of respiratory physiotherapy, especially for patients with chronic respiratory diseases.
Physical exercise helps improve overall endurance, lung capacity, and muscle strength, improving respiratory performance.
These exercises may include movements such as trunk rotations and spinal flexions, which focus on improving chest mobility and breathing.
Main benefits of respiratory physiotherapy
With the advances in respiratory physiotherapy and the development of different techniques, a number of benefits have been demonstrated for patients with lung conditions, including:
- Reduced breathing difficulty:
Respiratory techniques efficiently distribute air in the lungs, improving pulmonary ventilation and increasing respiratory capacity. This helps alleviate breathlessness and improves the lungs' ability to properly oxygenate the body.
- Improved blood oxygen levels:
Through improved ventilation and lung capacity, respiratory physiotherapy helps increase blood oxygen saturation, which reduces the sensation of fatigue and improves the patient's overall well-being.
- Prevention of chest deformities:
In many cases, respiratory physiotherapy helps improve the elasticity of the rib cage, preventing deformities in the chest, particularly for individuals with lung conditions.
- Improved quality of life:
Reduced dyspnoea (difficulty breathing), increased lung capacity, and greater independence in performing daily activities contribute to a significant improvement in the quality of life of patients.
Who can benefit from respiratory physiotherapy?
Respiratory physiotherapy is especially beneficial for patients with lung diseases, such as the following:
- Cystic fibrosis and bronchiectasis:
These diseases cause a chronic increase in mucus build-up in the lungs, which can make breathing difficult. Respiratory physiotherapy uses bronchial drainage techniques to prevent mucus build-up and improve breathing.
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD):
This disease includes conditions such as chronic bronchitis and pulmonary emphysema. Respiratory physiotherapy helps reduce mucus build-up and improves the balance between pulmonary ventilation and perfusion.
- Asthma:
In asthmatic patients, respiratory physiotherapy helps to prevent and control asthma attacks, while teaching patients to manage their condition effectively.
- Pneumonia and bronchopneumonia:
Respiratory physiotherapy helps to resolve mucus build-up in the lungs, aiding recovery.
- Neuromuscular and orthopaedic diseases:
Physiotherapy is also useful in patients with conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, pulmonary fibrosis, scoliosis, and other diseases that affect mobility and lung function.
Conclusion
Ultimately, respiratory physiotherapy is a vital discipline in the treatment of patients with lung disease and can significantly improve their quality of life.
Through a combination of specialised techniques such as respiratory exercises, bronchial drainage, and general physical training, physiotherapists can help patients manage and improve their respiratory conditions.
At Telic Group, we offer a wide range of solutions specifically designed for physiotherapy professionals, aiding the rehabilitation and care of patients in the process of physical recovery or treatment. Our products support physiotherapists, optimising therapeutic outcomes and ensuring patient well-being throughout the rehabilitation process.

 Español
Español Français
Français